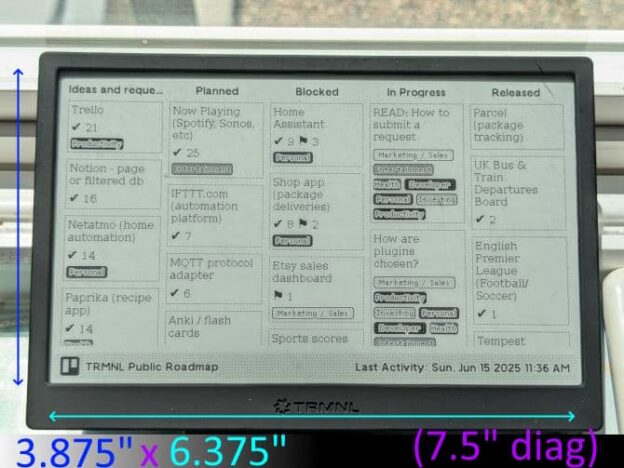
I fell for TRMNL on June 2, 2025. It felt fun to transform data with some easy coding and see it appear on a screen beautifully. The dopamine loop was short and the possibilities started flooding my brain. However, before I go too far, let’s get two somethings out of the way first.
My Biases
I have owned 4 variations of e-ink screens (Nook Touch 1st Gen, Waveshare NFC screens, reMarkarkable 2 tablet, and now a TRMNL). I do not hide how much of a joy it is to read, especially as my vision has, um, deteriorated after 40. Like life, the solution to readability is to add light; natural light when possible. I am a fanboy of e-ink technology itself.
E-Ink also doesn’t require power management at the scale of most modern devices. Plugging it in is a thing you forget to do because it’s so infrequent. It also feels like a trick because the last arrangement of pixels never fades, warps, or changes, instead enduring like a Roman aqueduct or a tombstone (in the case of my Nook Touch).
I have two children 5 and under and they are living in that gap where they are curious about the world, but are unable to be self-reliant on gathering that information because of learning limitations (reading words, understanding clocks, etc). Giving them independent opportunities to learn and grow requires different approaches, and this lens is constantly looking at my world and searching for new opportunities.
A $10 Off Coupon
Get $10 off a TRMNL device with the code: mario10
Full disclosure: I’ll also get $10… to buy more TRMNLs.
Continue reading →